Spam Emails and Spam Detection: We will help you write better emails
Intro
Spam creation and distribution is an extremely fruitful business because of the significance the web has achieved on people’s communication. Important info is being sent and received every second across computers on the Internet. Nobody wants important info ending up in wrong hands, because a button was clicked or a form submitted on a seemingly trustworthy site, after reading an email.

Spam Assassin, an Apache project, integrated to Tellody campaign creation mechanism, comes to solve the aforementioned problem.
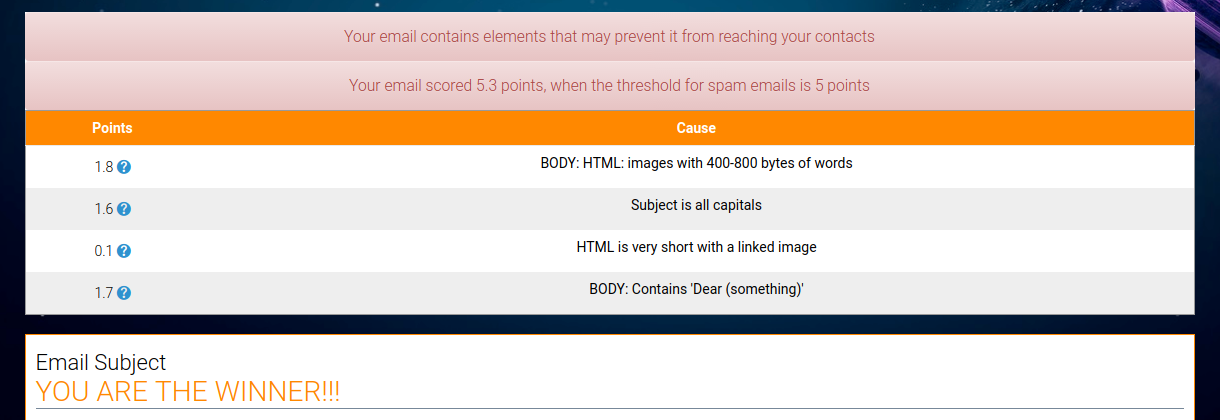
In the above image we demonstrate a portion of Tellody’s email creation page, where the list of spam rules, violated by the content of the example email, is placed.
The first rule violated in our example concerns the fact that the image embedded in our email was too big, meaning that in order to avoid text-based filtering, we chose to convey content via image instead of text. This violation provides 1.8 points to the total amount of points, which if exceeds the threshold of 5 points, then the message is considered spam and flagged as inappropriate. The scoring policy is basically arbitrary, but statistically inferred by spam assassin community. Next to every rule violation is a question mark to navigate the user to an explanation of this rule.

The next rule violated is the “all capitals” email subject. Many spam emails have subjects and bodies written in all capital letters, in order to emphasize their content or show urgency so as to make the user take immediate action avoiding critical thinking.
But, what happens when the text content we provide is too small and also includes an image? It is a well-known fact that spam emails tend to have a lot of images in order to emotionally trigger the users. Well we all want this desirable result, BUT this also is considered a violation.
The last rule violation in our example is the formal salutation/greeting of “Dear (someone) included in the text, which is a commonly used and generic way to address the recipient of the spam message.
In a nutshell, a bulk-messaging platform has to take the necessary precautions in order to prevent its users from making spam messages intentionally or unintentionally. Tools, such as Spam Assassin and others, assembled together into a safe-net layer make the platform more trustworthy and the web a “cleaner place”.






